
Капли датского короля
Капли датского короля.
Российская военная фармакопея, 1913 год.


Наше предприятие осуществляет заготовку, сушку и реализацию пряно-ароматического и лекарственного…
Европейская Фармакопея издание 7.0 часть 1 2010 год (Ph. Eur. 7.0) стр.1147-1148 Боярышника плоды
01/2008:1220 corrected 6.0
HAWTHORN BERRIES
Crataegi fructus
DEFINITION
Dried false fruits of Crataegus monogyna Jacq. (Lindm.), or Crataegus laevigata (Poir.) D.C. (synonym: Crataegus oxyacantha L.) or their hybrids or a mixture of these false fruits.
Content: minimum 1.0 per cent of procyanidins, expressed as cyanidin chloride (C15H11ClO6; Mr 322.7) (dried drug).
CHARACTERS
Sweet mucilaginous taste.
A. The false fruit of Crataegus monogyna is obovate or globular, generally 6-10 mm long and 4-8 mm wide, reddish-brown or dark red. The surface is pitted or, more rarely, reticulated. The upper end of the fruit is crowned by the remains of 5 reflexed sepals surrounding a small sunken disc with a shallow, raised rim. The remains of the style occur in the centre of the disc with tufts of stiff, colourless hairs at the base. At the lower end of the fruit is a short length of pedicel or, more frequently, a small pale circular scar where the pedicel was attached. The receptacle is fleshy and encloses a yellowish-brown, ovoid fruit with a hard, thick wall containing a single, elongated, pale brown, smooth and shiny seed.
The false fruit of Crataegus laevigata is up to 13 mm long. It contains 2-3 stony fruits, ventrally flattened, with short hairs at the top. Frequently, in the centre of the disc of the false fruit occur the remains of the 2 styles.
B. Reduce to a powder (355) (2.9.12). The powder is greyish-red. Examine under a microscope using chloral hydrate solution R. The powder shows the following diagnostic characters: covering trichomes from inside the disc which arelong, unicellular, frequently bent, tapering to a point, with smooth, much thickened and lignified walls; parenchymatous receptacle fragments, the outer layer with red colouring matter, some cells of the inner layers containing small cluster crystals of calcium oxalate ; occasional fragments including groups of sclereids and vascular strands with associated files of cells containing prisms of calcium oxalate ; pericarp fragments consisting of large thick-walled sclereids with numerous pits, some of which are conspicuously branched; a few fragments of the testa having an epidermal layer composed of hexagonal, mucilaginous cells beneath which is a yellowish-brown pigment layer containing numerous elongated prisms of calcium oxalate; thin-walled parenchyma of the endosperm and cotyledons containing aleurone grains and globules of fixed oil.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution. To 1.0 g of the powdered drug (355) (2.9.12) add 10 mL of methanol R and heat in a water bath at 65 °C for 5 min, shaking frequently. Allow to cool to room temperature and filter. Dilute the filtrate to 10 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution. Dissolve 2 mg of chlorogenic acid R, 2 mg of caffeic acid R, 5 mg of hyperoside R and 5 mg of rutin R in 20 mL of methanol R.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: anhydrous formic acid R, water R, methyl ethyl ketone R, ethyl acetate R (10:10:30:50 V/V/V/V).
Application: 30 pL of the test solution and 10 pL of the reference solution, as bands.
Development: over a path of 15 cm.
Drying: at 100-105 °C.
Detection: spray whilst hot with a 10 g/L solution of diphenylboric acid aminoethyl ester R in methanol R, subsequently spray with a 50 g/L solution of macrogol 400 R in methanol R; allow to dry in air for 30 min and examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results: the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution shows in the lower half, in order of increasing RF values, a yellowish-brown fluorescent zone (rutin), a light blue fluorescent zone (chlorogenic acid) and a yellowish-brown fluorescent zone (hyperoside); in the upper third appears a light blue fluorescent zone (caffeic acid).
The chromatogram obtained with the test solution shows 3 zones similar in position and fluorescence to the zones due to chlorogenic acid, hyperoside and caffeic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution, and 3 weak reddish fluorescent zones, one corresponding to the zone due to rutin in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution and both of the others located above the zone due to hyperoside. Below and above the zone due to caffeic acid some light blue zones appear.
TESTS
Foreign matter (2.8.2): maximum 5 per cent of deteriorated false fruit and maximum 2 per cent of other foreign matter. It does not contain fruits of other Crataegus species (C. nigra Waldst. et Kit., C. pentagyna Waldst. et Kit. ex Willd. and C. azarolus L.) which are characterised by the presence of more than 3 hard stones.
Loss on drying (2.2.32): maximum 12.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g of the powdered drug (355) (2.9.12) by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
Total ash (2.4.16): maximum 5.0 per cent.
ASSAY
To 2.50 g of the powdered drug (355) (2.9.12) add 30 mL of ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R. Heat under a reflux condenser for 30 min and filter. Wash the residue with 10.0 mL of ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R. Add to the filtrate 15.0 mL of hydrochloric acid R1 and 10.0 mL of water R. Heat under a reflux condenserfor 80 min. Allow to cool, filter and wash the residue with ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R until the filtrate is colourless. Dilute the filtrate to 250.0 mL with ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R. Evaporate 50.0 mL of this solution in a round-bottomed flask to about 3 mL and transfer to a separating funnel. Rinse the round-bottomed flask sequentially with 10 mL and 5 mL of water R and transfer to the separating funnel. Shake the combined solution with 3 quantities, each of 15 mL, of butanol R. Combine the organic layers and dilute to 100.0 mL with butanol R.
Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the solution at 545 nm. Calculate the percentage content of procyanidins, expressed as cyanidin chloride, using the following expression:
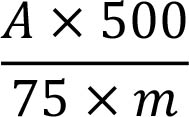
i.e. taking the specific absorbance of cyanidin chloride to be 75.
A = absorbance at 545 nm,
m = mass of the substance to be examined, in grams.